From the Archives
By Mary Woodward
JACKSON – In the last article we visited with some statues that had found new homes after being displaced. This week I would like to introduce you to a couple of crucifixes that are connected with two churches dedicated to the Blessed Mother.
First, we have the crucifix that adorned St. Mary Church in West Jackson. The parish was merged with St. Therese Parish in 2015. St. Mary Church was completed in the mid-1950s and stood regally on Claiborne Avenue for 60 years, but early on Yazoo Clay began to take a toll on the foundation of the structure. The rise of suburbia took a toll on the size of the congregation and ultimately the difficult decision was made to close St. Mary’s and merge it with St. Therese.
We featured St. Mary’s statues previously as mentioned, but the actual dismantling of the high altar and finding a home for the crucifix that graced it was a daunting challenge. Eventually, we made contact with Father Tommy Conway of the Diocese of Biloxi, who was tasked with establishing a new parish ironically in a suburb outside of Hattiesburg.
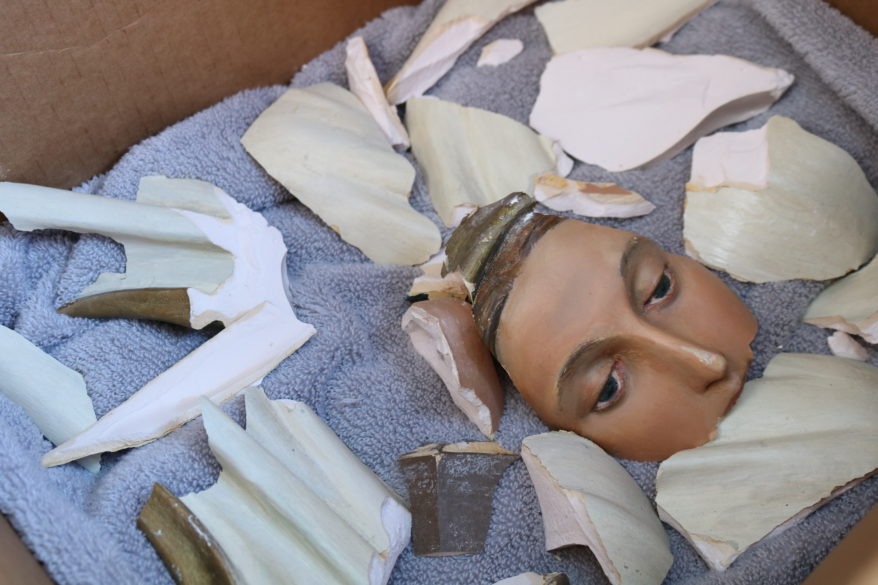
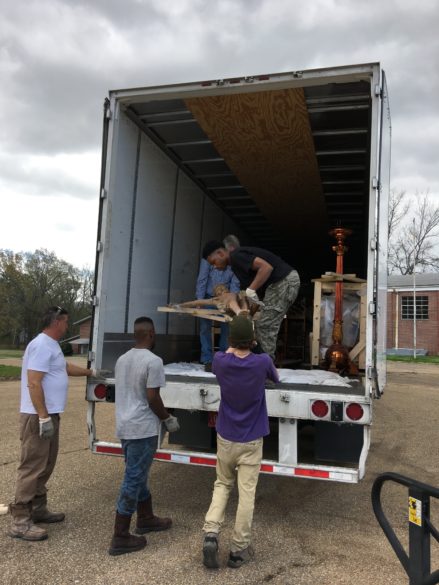
The corpus was wooden with a long crack down the torso. It was attached to one-inch-thick green now very brittle marble. Therefore, the corpus was removed separately and mounted to a wooden frame for transport to the new parish which was dedicated to St. Fabian.
It was the last item loaded into the 18-wheeler full of crated marble, tabernacle, and candlesticks. As in Caravaggio’s Deposition, the salvage crew reverently carried the Crucified Christ to the bed of the trailer and gently laid him down on a padded cloth. The door slid down like the stone rolled before the tomb.
I have to say it was a very powerful moment for all of us working there that morning. Watching the truck pull away knowing the Lord was entombed in it brought a silence upon us and tears trickled out of the corner of eyes down cheeks.
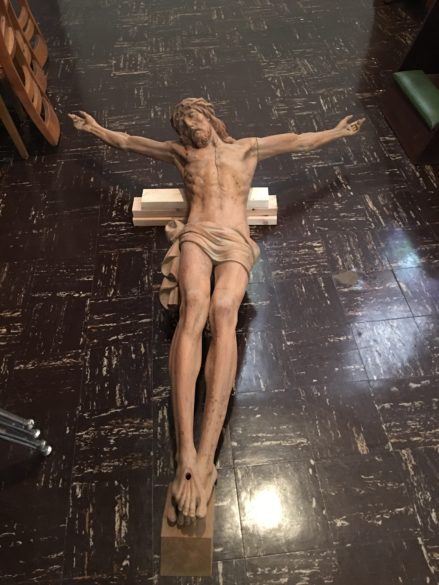
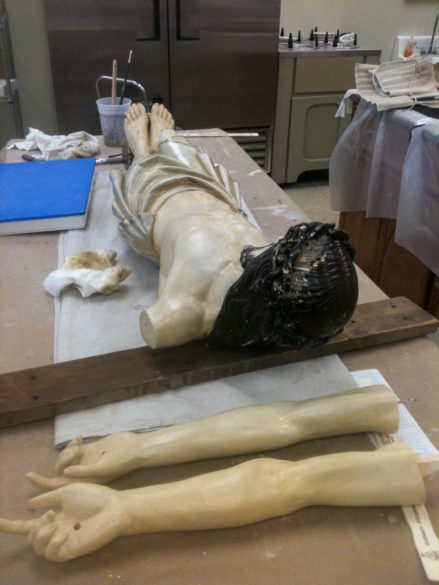
Our second featured crucifix now hangs on the wall in the St. Mary Basilica family life center in Natchez. In early 2012, the crucifix was discovered by Basilica Archives Committee members in the original crypt area in the lower level of the church. It was mounted on a wall and showed the signs of its age and a few botched repair efforts.
One of the wonderful aspects of archives life is the people one encounters. St. Mary Basilica Archives Committee is a group of extremely dedicated individuals who have taken the reins of creating an amazing local archive, which is a shining example of love for our faith and our traditions.
Immediately the committee, led at that time by Chairman Jimmy Guercio, resolved to have the sacred object researched and restored. According to an article by Guercio on the Basilica Archives web page, there was no real documentation on the crucifix anywhere. The only mention of a large crucifix being in the church was from Bishop William Henry Elder’s note dated May 3, 1869, that a “blessed nail” was “preserved in the Sacred Feet of the large crucifix…in the Cathedral…”


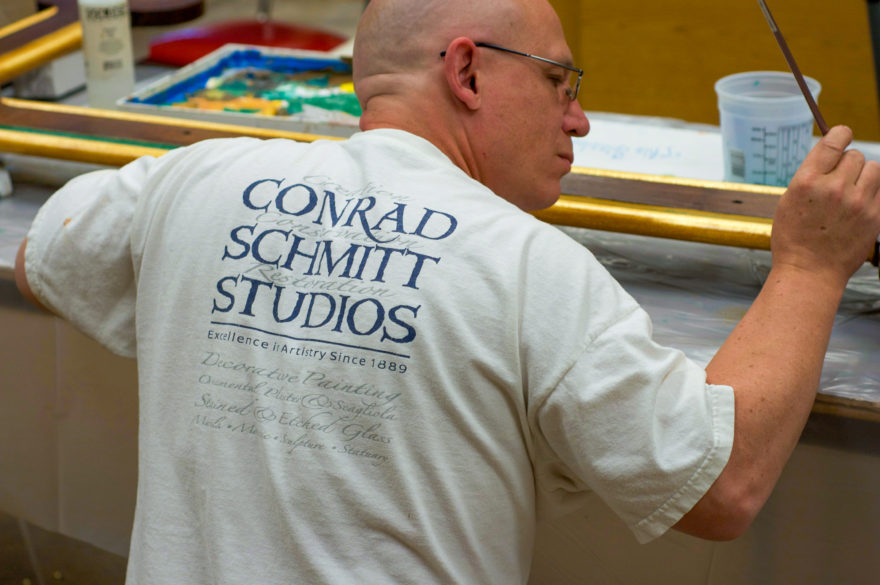
Coincidentally, the Conrad Schmitt design and restoration company, which had restored the Basilica in 2001, was wrapping up its renovations of the Cathedral in Jackson. Wil Kolstad, the lead artisan for the Cathedral project, was sent to Natchez to restore the crucifix.
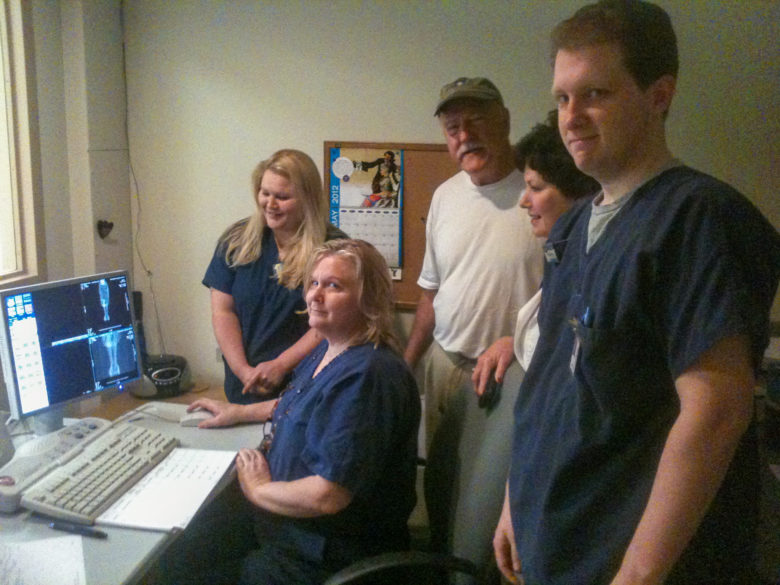
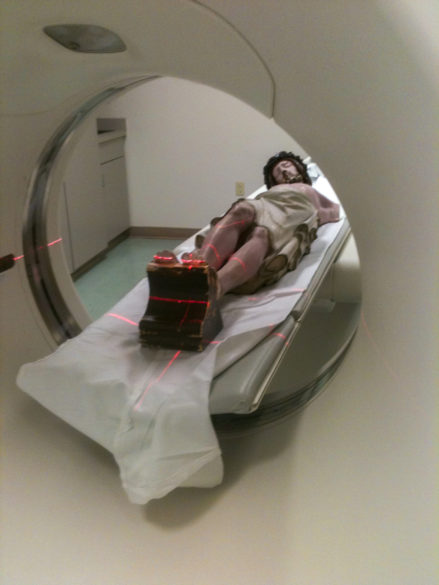
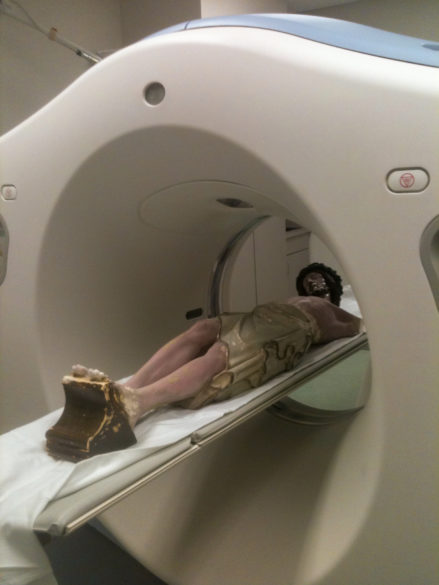
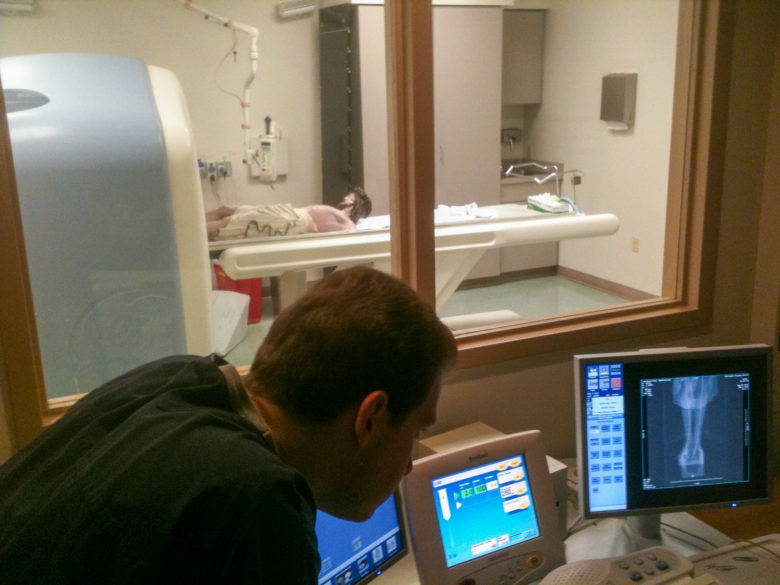
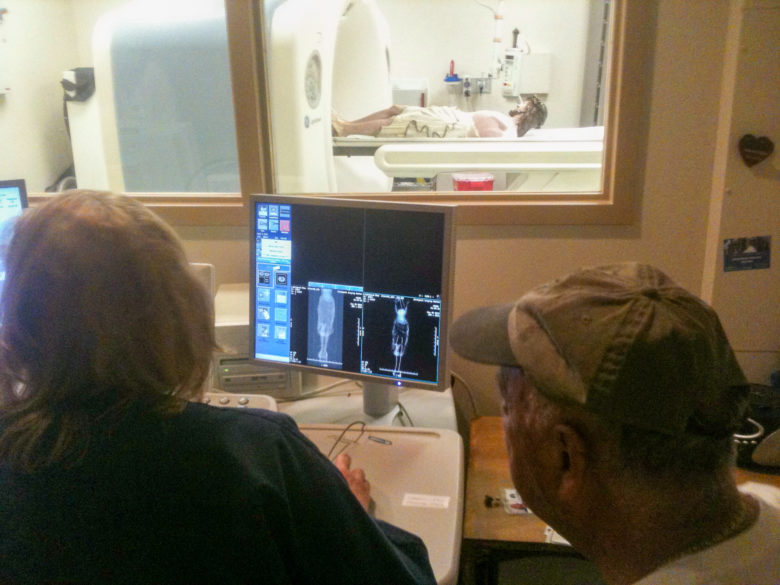
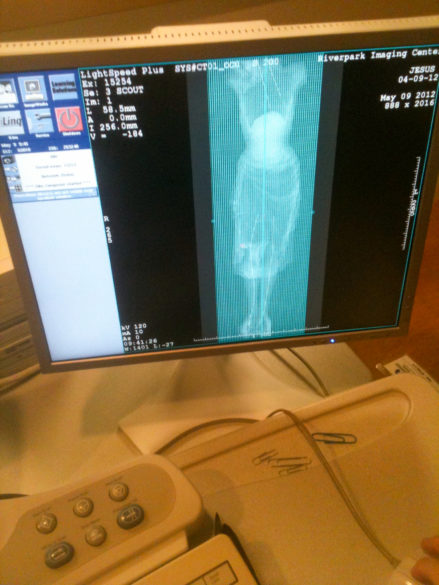
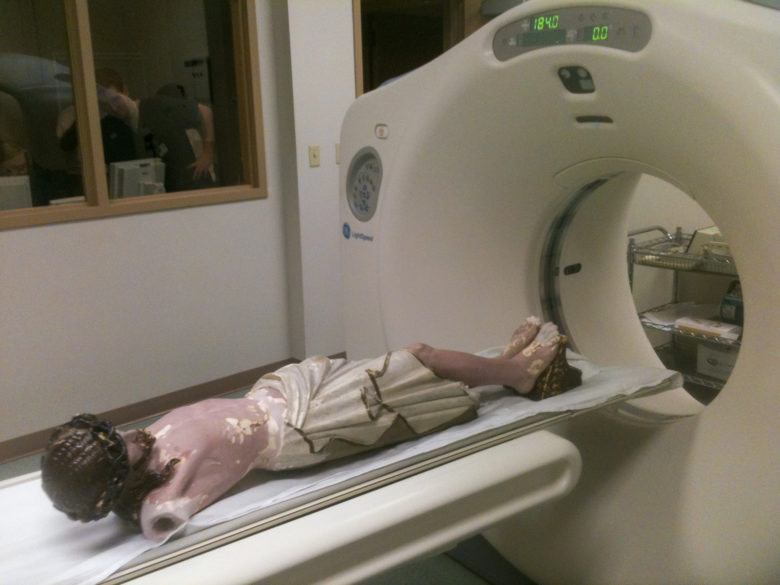
Prior to completing the process, the mystery of the blessed nail needed to be solved. Therefore, Guercio, Kolstad and other committee members accompanied the corpus across the river to a diagnostic imaging center in Vidalia. The whole process of the patient Jesus being scanned was documented by committee photographer Mike Murphy.
Unfortunately, the scan did not reveal a nail in the feet, but it does reflect the fine dedication of the Basilica Archives Committee and its commitment to document the faith and tradition of the church of Natchez and our diocese. I hope these accounts of our sacred objects will inspire in you, the reader, a sense of Catholicity and a love for the deep and sacred spiritual traditions of our church. There is nothing else like it on this earth; it can only be heaven sent.
(Mary Woodward is Chancellor and Archivist for the Diocese of Jackson)